Healthy Normal Vision and Visual Defects

Healthy Normal Vision
With normal healthy vision, everything you see is clear and in focus. Many people refer to this as 20/20 vision. You can see all objects clearly, whether they are close up or in the distance. This is a normal healthy eye.
In order to see, there must be light. Light reflects off the object and enters the eye. The light passes through the clear covering on the eye called the ‘cornea’. That helps focus light through the pupil.
Next, the light passes through the crystalline lens which constricts to help light rays focus on point on the retina resulting in clear vision.
Visual Defects
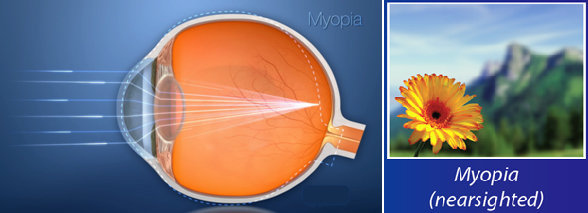
Myopia or Nearsightedness
Myopia or Nearsightedness means that you can clearly see objects that are close to you, but distant objects are blurry.
Myopia occurs when the eye is larger and has a longer depth than an average eye. Since the eye is longer than average, the light that is focused in the eye lands in front of the retina rather than directly on the retina. However, Myopia can be corrected by applying Excimer laser treatment in the center area of the eye allows the light rays to arrive at one point on the retina, correcting the myopia and giving you clear vision.
Hyperopia or Farsightedness
Hyperopia or Farsightedness means that you can see distant objects clearly, but objects that are closer to you are blurry.
Hyperopia occurs when the eye is smaller and has a shorter depth than an average eye.
When light enters an eye with hyperopia, the light rays focus behind the retina rather than directly on the retina. Most cases with hyperopia can be corrected. An Excimer laser treatment around the center of the eye will allow light rays to arrive at one point on the retina, correcting the hyperopia and improving your vision.

Astigmatism
With a healthy normal eye, the shape of the cornea is spherical like a ball. This allows light to pass through the lens without distortion. Light rays focus properly on the retina to provide the sharp image of what you are seeing.
With ‘Astigmatism’, the cornea has more of an oblong shape, like an oval, causing light to bend and distort as it passes through the lens. This makes object appears blurry or unfocused at all distances because light rays are not focus on one spot to provide clear vision. An Excimer laser treatment will address the astigmatism to allow the light rays to arrive at the retina and provide you with clear vision.

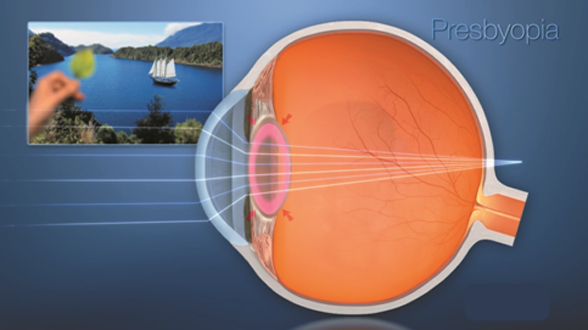
Presbyopia
Much like adjusting the focus of a camera, in a healthy eye, the lens flexes and changes shape to properly focus on objects at different distances. However, as your eye age, they lose the ability to flex. The result is diminished up close vision. This is called ‘Presbyopia’. Presbyopia is a natural part of aging.Patients who have had LASIK earlier in their lives should know that the treatment isn’t wearing off, but the crystalline lens isn’t allowing them to continue to see images up close the same way they used to.
Good Candidates for LASIK
- Over 20 years of age
- Candidate’s vision must be stableor change not more than 50 (0.5D) for at least one year
- No other eye diseases such as severe dry eye, eye inflammation, Diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid, SLE
- Has a good understanding about laser vision correction surgery
Preparation for Eye Examination
These are steps to examine patient’s eyes before receiving LASIK surgery.
- Require 2-3 hours for eye examination
- Soft contact lenses wearer has to cease wearing for at least 7 days
- Hard contact lenses wearer has to cease wearing for at least 4 weeks
- Bring your relative or friend along with you on the eye examination day because your eyes will be dilated by eye drops which will cause blurry vision and cannot tolerate to bright light.
Procedures of Eye Examination before LASIK
- Visual acuity
- Intraocular pressure
- Fundus examination (Retinal examination)
- Anterior and posterior corneal curvature (Schwind Sirius)
- Corneal thickness (Pachymetry)
- Refractive error (Wavefront Analyzer)
- Tears quantity (Schirmers Test)
